Appearance
webpack插件架构
Webpack5 暴露了多达 200+ 个 Hook,基本上覆盖了整个构建流程的所有环节 —— 这也就意味着通过编写插件,我们几乎可以改写 Webpack 的所有执行逻辑
Compiler
全局构建管理器,Webpack 启动后会首先创建 compiler 对象,负责管理配置信息、Loader、Plugin 等。从启动构建到结束,compiler 大致上会触发如下钩子:

createChildCompiler:创建子 compiler 对象,子对象将继承原始 Compiler 对象的所有配置数据;createCompilation:创建 compilation 对象,可以借此实现并行编译;close:结束编译;getCache:获取缓存接口,可借此复用 Webpack5 的缓存功能;getInfrastructureLogger:获取日志对象; 等等。
Compilation
单次构建过程的管理器,负责遍历模块,执行编译操作; 当 watch = true 时,每次文件变更触发重新编译,都会创建一个新的 compilation 对象; compilation 生命周期中主要触发如下钩子:
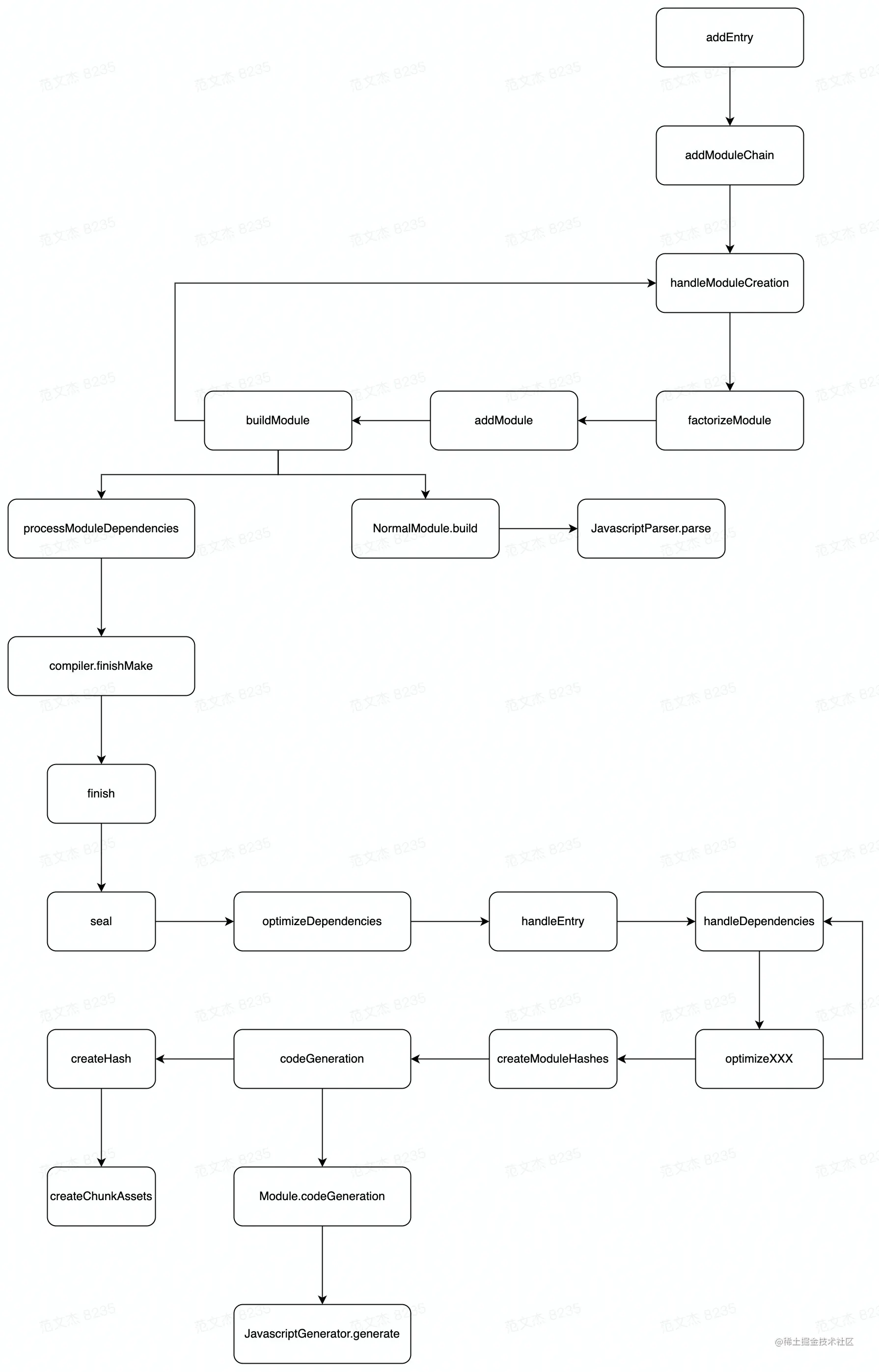
addModule:用于添加模块,例如 Module 遍历出依赖之后,就会调用该接口将新模块添加到构建需求中;addEntry:添加新的入口模块,效果与直接定义 entry 配置相似;emitAsset:用于添加产物文件,效果与 Loader Context 的 emitAsset 相同;getDependencyReference:从给定模块返回对依赖项的引用,常用于计算模块引用关系;assets: 产物列表, 调用 asset.source() 方法读取产物内容jsconst assetSource = asset.source() // ... compilation.assets[filename] = new RawSource(xxx)const assetSource = asset.source() // ... compilation.assets[filename] = new RawSource(xxx)warnings,errors:收集日志jscompilation.warnings.push('xxx') compilation.errors.push('xxx')compilation.warnings.push('xxx') compilation.errors.push('xxx')
Module
资源模块,有诸如 NormalModule/RawModule/ContextModule 等子类型,其中 NormalModule 使用频率较高,提供如下接口:
identifier:读取模块的唯一标识符;getCurrentLoader:获取当前正在执行的 Loader 对象;originalSource:读取模块原始内容;serialize/deserialize:模块序列化与反序列化函数,用于实现持久化缓存,一般不需要调用;issuer:模块的引用者;isEntryModule:用于判断该模块是否为入口文件; 等等。
Chunk
模块封装容器,提供如下接口:
addModule:添加模块,之后该模块会与 Chunk 中其它模块一起打包,生成最终产物;removeModule:删除模块;containsModule:判断是否包含某个特定模块;size:推断最终构建出的产物大小;hasRuntime:判断 Chunk 中是否包含运行时代码;updateHash:计算 Hash 值。